Monday, 13 September 2021
Explain Viva of Electrostatics | physics
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Sunday, 7 March 2021
With the help of a neat diagram | explain the reflection of light from the plane reflecting surface on the basis of wave theory of light.
So here first of all we know that,
What is the laws of reflection :
i) In the laws of reflection, the incident rays, reflected rays, and normal to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same level.
ii) In the laws of reflection, the incident rays and the reflected rays lie on the opposite sides of the normal.
iii) The angle of incidence is equal or we can say equivalent to the angle of reflection.
For clear understanding the law of reflection in simple and easy way. So for that lets see the simple explanation about all these points.
Explanation :
i) The plane wavefront AB is developing at an angle towards plane reflecting surface XY.AA1 and BB1 are incident rays.
ii) When point 'A' come to XY at A1, than ray at 'B' reaches at point P and it has to cover distance PB1 to reach the reflecting surface XY.
iii) Let's consider 't' be the time to required to cover distance PB1.
In this time meantime, the secondary waves are emitted from the point A1 and it will spread over the hemisphere of the radius A1R in the same medium.
The distance covered by the secondary waves to reach from A1 to R in time 't' is same as the distance covered by the primary waves to reach from point P to B1.
So therefore A1R = PB1 = ct.
iv) All other rays in between AA1 and BB1 will reach XY after A1 and before B1. Therefore they will also emits secondary waves of the decreasing radii.
v) The surface touch all such hemispheres is RB1 which is reflected wavefront, bounded by the reflected rays A1R and B1Q.
vi) Let's draw A1M perpendicular to XY and B1N perpendicular to XY.
Thus, the angle of incidence is angle AA1M = angle BB1N = i and the angle of reflection is angle MA1R = angle NB1Q = r.
angle RA1B1 = 90 - r
angle PB1A1 = 90 - i
vii) In the triangle A1RB1 and triangle A1PB1
Here angle A1RB1 congruent to angle A1PB1
A1R = PB1,............ (Reflected waves travel in equal in same medium in equal time).
A1B1 = A1B1.........(Common side)
Therefore triangle A1RB1 congruent to triangle A1PB1
Therefore angle RA1B1 = angle PB1A1
Therefore 90 - r = 90 - i
Therefore i = r
viii) From the above given figure, it clear that the incident ray, reflected ray and normal lie in the same level or plane.
ix) This laws of reflection of light from the plane reflecting surface on the basis of Huygen's wave theory.
THE END
Thank you
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Saturday, 6 March 2021
The Huygen's construction of spherical wavefront in simple and easy way !!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
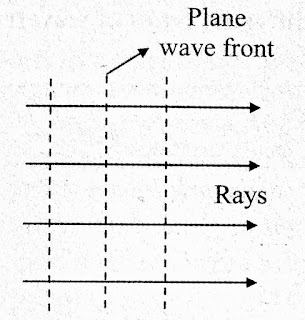
Explain the Huygen's construction of plane wavefront in easy and simple way !!!
Explain the Huygen's construction of plane wavefront in easy and simple way !!!
So let's come to know,
i) The plane wavefront is formed when the point of observation is very far away or we can say at infinity from the primary source of light.
ii) So here let's PQR represent a plane wavefront at any instant.
So according to the Huygen's principle, all the points on this wavefront will act as a secondary source of light and sending out secondary wavelets in the forward direction only.
iii) For make it to undestand easily, first of all we need to draw hemisphere with Point P,Q,R.... as centres and 'ct' as a radius.
The surface tangential to all such hemisphere is P1Q1R1....at instant 't'.
The new wavefront at time 't'.
iv) The plane wavefront is propagated or travel as a plane waves in the homogeneous isotropic medium. Therefore they are parallel to each other.
v) PP1N1, QQ1N2, RR1N3 these are the wave normal at point P,Q,R respectively.
These wave normal shows the direction of propagation of the plane wavefront.
vi) The new wavefront P1Q1R1 is parallel to the primary wavefront PQR.
THE END
Thank you....!!!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Difference in between primary source of light and secondary source of light in easy way !!!
Primary source of light
i) The primary source of light is a real source of light.
ii) Primary source of light sends out primary waves in the all possible directions.
iii) The primary source of light is effective at every point on it's surface.
iv) The primary source of light is situated in the air.
The secondary source of light
i) The secondary source of light is a fictitious source of light.
ii) The secondary source of light sends out secondary waves only in the forward direction.
iii) The secondary waves is effective only at the points where it touches the envelope.
iv) The secondary source of light is situated on the wavefront.
THE END
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Friday, 5 March 2021
State what are the Huygen's principle statement !!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
State and explain the main characteristics of the wavefront in easy and simply way.
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
What is the expecting wavefront shape when the portion of the wavefront of light from a distant star intercepted by the earth ?
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Thursday, 4 March 2021
What is the expecting shape of the wavefront when light emerging out of a convex lens ?
Hello dear all readers,
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
What is the expecting shape of the wavefront when light diverging from a point source ?
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Wednesday, 3 March 2021
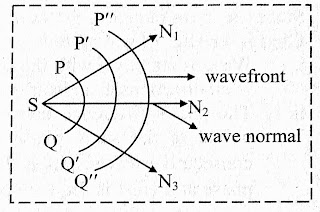
What are the main characteristics of the wave normal !!!
Hello dear all readers,
Welcome to this concept, so here in this concept you come to know about the main characteristics of the wave normal in easy and simple way.
So let's come to our topic,
i) The wave normal gives the direction of propagation of wave.
Let's take an one example, the medium through which wave is propagated, for an example 'air' so the wave is move in the direction of air simply.
Actually medium or we can say channel gives the direction for propagation of wave.
So it means that, the wave normal work according to the medium through which is allow to propagate.
ii) The wave normal is perpendicular to the wavefront.
Explanation : As you can see in the given image, the wave normal is perpendicular to the wavefront.
It means that, the wave normal make an angle with wavefront is 90° Degree.
iii) In a homogeneous isotropic medium, the wave normal is same as direction of ray of light.
Explanation : In a homogeneous isotropic medium or channel, the wave normal is same as direction of light.
It means that , First of all we have to know that, what is homogeneous ?
Homogeneous : Homogeneous is a uniform structure.
Isotropic material : The isotropic material whose properties remains same when tested in different different directions.
When we allow to propagate wave normal in the Homogeneous isotropic medium then the direction of the wave normal is in the direction of ray of light.
iv) Wave normal is drawn from the point of generation of wavefront.
Explanation : Actually the wave normal is start from the point where wavefront is generated.
So we hope you understand this concept very simply and easily.
If you have any doubt related to this concept than feel free to ask us.
We feel good to reply you as soon as possible.
Goodbye !!!
Thank you...!!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Tuesday, 2 March 2021
State the different types of wavefront with suitable examples !!!
Hello dear all readers,
Welcome to this concept, so in this concept you come to know the different types of wavefronts with examples.
So let's explore this concept !!!
The wavefront is three types,
i) Spherical wavefront
ii) Plane wavefront
iii) Cylindrical wavefront
So let's know about this different wavefronts with an examples !!!
i) Spherical wavefront : The wavefront which is originating from a point source of light at some finite distance is called as or known as 'spherical wavefronts'
The example of this spherical wavefronts is : The candle flame, which we use in our day to day life in the moments such as birthday, marriage anniversary, or when electricity cut off.
The candle flame glow in the form of spherical wavefront.
ii) Plane wavefront : The wavefronts which is originating from a point source of light at infinite distance is called as or known as 'plane wavefront'.
The example of this plane wavefront is : The light from the sun arrives at the surface of the earth in the form of plane wavefront.
iii) Cylindrical wavefront : The wavefront which is originating from the linear source or slit of light at some finite distance is called as or known as 'cylindrical wavefront'.
The example of this cylindrical wavefront is : When a tube light is glow, it glow in the form of 'cylindrical wavefront'.
So we hope you understand this concept in simply and nicely.
So if you have any query related to this concept than feel free to ask us.
If in your mind have any idea to know something in simple and easy way than write in the comment box.
Good bye !!!
Thank you...!!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Sunday, 28 February 2021
Know complete kepler's laws of planetary motion in simple and easily | By scientechplus
Welcome to this new concept, so here in this concept you will come to know about all kepler's law of planetary motion.
So let's start to know the concept,
So first of all we know that the kepler's first law,
For understanding this kepler's law of planetary motion, first of all we need to know about, what is ellipse ?
So if we talk about ellipse than this ellipse have two foci or we can say two focus point.
This foci is same measure from the centre of the ellipse.
The longer foci diameter is known as or called as 'major axis'.
And the smaller foci diameter is known as or called as 'minor axis'.
So as like that, at one foci the sun is situated and rest of all planet revolve around the sun in elliptical orbit motion.
The second law of kepler's planetary motion : The second kepler's law state that, the line joining the planet and the sun sweeps equal areas in equal interval of time.
The planet which moving from point A to point B and the planet which move from point C to point D, according as you can see in the above given image, so if we calculate both cover area by the planet is same in equal interval of time.
So let's say if we consider, the planet cover 10 metre square in 2 minutes than so in the coming 2 minutes the planet will also cover only 10 metre square area.
I mean to say that, the planet cover equal area in equal interval of time not equal distance.
So this is only possible because of according to the kepler's suggested statement on, "A planet moves faster when it is closer to the sun and the planet moves slowly when it is farther from the sun".
So you have one question arises in your mind that, how it is possible when planet come closer to the sun it moves faster and when it farther from the sun it become slow ?
So the answer is : It is only because of gravitational pull.
When as planet arrives closer to the sun the gravitation pull become more and when the planet farther from the sun the gravitational pull become less.
The third law of kepler's planetary motion : The kepler's third law state that, the square of it's period of revolution around the sun is directly proportional to the cube of the mean distance of a planet from the sun.
The planet as much as time take to revolve around the sun, so square of that time and this is equal to the cube of it's semi major axis.
So we hope you understand this concept very clearly and nicely.
If you have any query related to this concept than please fell free to ask us.
So we will meet you with next upcoming interesting concept.
Goodbye !!!
Thank you...!!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Define about wavefront, wave normal and wave surface in simply and easily | By scientechplus
Hello dear all readers,
Welcome to this concept, so here in this concept you come to know the definition about wave front, wave normal and wave surface.
So let's define first of all 'wavefront'
i) Wavefront:- The locus of all the points of the medium to which waves reach simultaneously so that all the points are in the same phase or we can say all the points in same state of vibration is called as or known as 'wavefront'.
And the second is 'Wave normal'
ii) Wave normal:- A perpendicular line drawn to the surface of a wavefront at any point of the wavefront in the direction of propagation towards light waves is called as or known as 'wave normal'.
And the last third is 'Wave surface'
iii) Wave surface:- The surface of a sphere with light source as centre and distance travelled by light waves as radius where each waves reach simultaneously is called as or known as 'wave surface'.
So we hope you understand this concept very simply and nicely.
So we will meet you in next upcoming interesting concept.
Goodbye !!!
Thank you...!!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Thursday, 18 February 2021
When we see at night in sea or in ocean the level of water goes up and in day time, the level of water goes down !!! Why it is happen ???
When we see at night in sea or in ocean the level of water goes up and in day time, the level of water goes down !!! Why it is happen ???
Welcome to this concept, here in this concept you come to know the most interesting and exciting concept, which delights your mood at high level.
So friends what are we waiting for,
Let's explore this concept in simply and easily !!!
In during holiday's when we go to picnic at beaches or spending some lovely moment at seashore.
Or you have experience this great moment when you go for camp in seashore side.
When we go for camp, we have to spend some days, isn't it ?
So in these camp days, we got to experience both day and night.
Have you observed any changes happening in the sea in day and night ???
If you observed and changes happening in sea during day and night ? Than please tell us in the comments box !!!
So let's know what actually happen during day and night time in sea.
You are very familiar with high tide and low tides that occur regularly in the sea , isn't it ?
The level of sea water goes up means that, it is called as high tide and the level of sea water is goes down it means, it is called as low tide.
It means clearly that, during night time we see moon, isn't it ?
When the moon come in contact directly with sea water than the level of water goes up.
It is because of moon's gravitational force.
So you know that here very clearly in during day time, the moon not come in contact directly with sea water.
That's why the water level of sea is goes down. It's means that in day time there is no gravitational force act on sea water.
Therefore, the level of sea water is goes down.
Here as you see in the above image, so in this image you very clearly see that low tide and high tide.
Where as in this image, the point (A) and point (B) represent the low tide.
Whereas point (C) and point (D) represent the high tide.
So we hope you enjoying in this concept and understand this concept very clearly and simply.
In your mind have any question or any concept than feel free to ask us.
So we will meet you with new upcoming interesting concept.
Goodbye !!!
Thank you...!!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Sunday, 14 February 2021
What are the merits and demerits of the 'Huygens' wave theory of light in easy and simple way !!!
Welcome to this new blog post concept, here you come to know that the merits and the demerits of the 'Huygens' wave theory of light.
So let's explore this concept in simply and easily,
So first of all we know about merits of 'Huygens' wave theory of light.
Merits of 'Huygens' wave theory of light !!!
i) Huygens gives sufficient explanation for the laws of reflection, refraction and double refraction of light by assuming transverse nature of the light waves.
ii) Huygens also explain the theory of interference and diffraction.
iii) The velocity of light in the rarer (air) medium is high and the velocity of light in the denser medium (water) is low so this is experimentally proved.
So let's know about the demerits of 'Huygens' wave theory if light.
Demerits of 'Huygens' wave theory of light !!!
i) Huygens wave theory of light could not explain about the rectilinear propagation of light.
ii) Huygens could not explain about polarization of light, Compton effect, photoelectric effect and etc.
iii) Huygens could not explain about the property of propagation of light through in the vacuum.
The reason behind this is, the ether has high elastic constant and zero density which gives contradictory results.
iv) According to the Huygens wave theory of light, they tell in his theory that, the 'luminiferous' ether medium is present or we can say exist every where in the universe.
And they also tell in his theory that, the 'luminiferous ether medium' also present or exist in the vacuum.
For the material medium propagation of light wave.
However, The Michelson's and the Morley's theory proved wrong to the presence or existence of the 'luminiferous ether medium' every where in the universe and even vacuum.
So we hope you understand this concept in easy and simply way.
So we will meet you with new upcoming concept.
Goodbye !!!
Thank you...!!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Saturday, 13 February 2021
Here you come to know about the 'wave theory of light by Huygen's
Welcome to this new concept, here in this concept you come to know that, the theory given by Huygen on the wave theory of light.
So let's explore this concept,
i) The source of light propagated light energy in the form of waves : In these statement, they tell us that, the particles of the medium vibrate about it's mean place in the form of simple harmonic motion.
Because of that , the particles can transfer energy from one particles to it's neighbouring particles and than reach to the observer eye.
ii) In the homogeneous isotropic medium, the velocity of light wave as it is or remains constant : The speed of the light wave is not affected because of, the density and the temperature of isotropic medium is remains same throughout.
iii) The different different colours of light waves is because of different different wavelength of light waves : We know that each light wave has it's own wavelength, isn't it ? So as we change it's wavelength than automatically it's colour and frequency also changes.
iv) There is the need of material medium for the propagation of light wave : Huygen theory states that, the periodically disturbance is created in the medium, when the light wave travel in the medium.
So to avoid the periodic disturbance, Huygens explain the propagation of light waves through vacuum.
Huygens suggested that the existence of a Hypothetical medium, which is called as or known as 'luminiferous ether'.
So in the Hypothetical medium there is almost negligible disturbance is created for propagation of light wave.
So these medium contain no any disturbance, when propagation of light waves.
So hey friends hope you enjoying to learn this session simply and clearly.
We will meet you with new concept.
So goodbye !!!
Thank you...!!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Friday, 12 February 2021
Known the drawbacks of Newton's corpuscular theory
Known the drawbacks of Newton's corpuscular theory !!!
Welcome to this new concept, here in this concept you come to know the drawback of Newton's corpuscular theory.
Earlier in our concept we discuss about the Newton's corpuscular theory.
But here in this concept we come with it's drawback.
Here we will know the all drawback of Newton's corpuscular theory in easy any simple way !!!
So let's come to our topic,
In the Newton's corpuscular theory, he could not able to explain about the partial reflection and refraction at the surface of the transparent medium or path.
In the Newton's corpuscular theory he could not explain about the phenomenon such as interference, diffraction, polarization etc.
According to the Newton's corpuscular theory he explain that, the speed of light in the denser (water) medium is more and the speed of light in the rarer (air) medium is less after which was experimentally proved wrong by the 'scientist Focault'.
According to the Newton's corpuscular theory, he explain in his theory that, when the particles are emitted from the source of light, than the mass of the source of light must be decreases but after conducted several experiments there is not shown any changes in the mass of the source of light.so here also failed the Newton's corpuscular theory.
So we see all the drawback and the given theory which could not explain by Newton's corpuscular theory.
This is all about the drawback of the Newton's corpuscular theory.
So we hope you understand this concept very clearly and nicely.
If you have any query related to this concept you can frequently ask question related to this.
So we will meet in the next upcoming concepts.
Thank you...!!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
State the postulates of Newton's corpuscular theory !!!
State the postulates of Newton's corpuscular theory !!!
Hello dear friends,
here we go to learn and know about the postulates of Newton's corpuscular theory.
So what are we waiting for ?
Let's explore this concept !!!
i) Every source of light energy emits large number of tiny particles is called as or known as 'corpuscles' in a medium surrounding the source.
ii) These tiny particles emitted by source of light are perfectly elastic, rigid, and weightless.
iii) The tiny particles which are emitted by source of light is travel in a straight line with very
high speed and the speed is vary according to different in different media or we can say path.
iv) One gets a sensation of light, when the corpuscles fall on the retina of eye.
v) The different colours of light are because of different sizes of corpuscles.
Explanation: i) So in the first paragraph, the Postulates of Newton's corpuscular theory want to tell us that, in our environment or in our surrounding every source of light energy emits large number to tiny particles.
Let's say in our planet Earth, the only one source of light energy is sun.
Have you imagine this, how much of tiny particles come out from the sun.
No idea ?
Here the answer is, the sun is a one type source of light energy.
Which means it's emits large number of particles.
You might be ask that, we doesn't seen any tiny particles.
Yes of course we admit it.
You not able to see the tiny particle but you can see the rays of the sun in the early morning.
ii) In the second paragraph, they want to tell us that, these
tiny particles are in perfectly in elastic, rigid and weightless form.
Elastic means stretchable.
Rigid means toughness.
Weightless mean No weight of these tiny particles.
iii) In the third paragraph, they want to tell that, these light tiny particles travel in a straight line with very high speed. And one thing also make in this is, the speed of tiny or smallest particles are different in different in media or in path.
iv) In the fourth paragraph, they want to tell us that, when these tiny particles fall on the retina of our eye than we get sensation therefore our eye automatically close.
v) And in the last paragraph they want to tell us that, the different different colours of light is all possible because of different sizes of corpuscles.
So we hope you understand this concept in easy and simply way.
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Friday, 29 January 2021
Distinguish or differentiate between free vibration and force vibration
Distinguish between or differentiate between free vibration and force vibration
Free Vibration
i) In the free vibration, this free vibration produce when a body is disturbed from it's equilibrium position.
ii) When we have to start the free vibration, than only initially required force to start the free vibration.
iii) The frequency of these free vibration is depended only on the natural frequency.
iv) In the free vibration, the energy of the body remain constant or remains as it is, in the absence of friction force, air resistance, etc.
Due to the damping force, the total free vibration energy get decreases.
v) The amplitude of the free vibration get decreases according with time.
vi) The free vibration, stop vibrating sooner or later depending on the damping force.
Force Vibration
i) The force vibration are produced when we apply an external periodic force of any frequency on it.
ii) The continuously external periodic force is requires for the force vibration. If we will stop applying of an external periodic force on force vibration than force vibration will also stop.
iii) The frequency of force vibration is depended only on the frequency of the external periodic force.
iv) The energy of the body is maintained or we can say in other words that, the energy of the body remains constant by the given external periodic force.
v) The amplitude of force vibration is get small with time but remains constant as external periodic force acts on it.
vi) The vibrations get stop as soon as external periodic force is stopped.
So we hope you understand this concept very clearly and nicely in great understanding way.
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Popular Posts
-
Ans : 1) This method cannot give the error, if inputs are other than the 3 standard test inputs. 2) Most of the times, this method gives ma...
-
The Applied Electronics MCQ || Test Revision paper !!! 1) The types of coupling used in the BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) amplifier. a)...
-
Controlled Rectifier: i) When SCR are used to convert AC to DC they have controlled output voltage, so it is called a controlled rectifier...
-
x2 – 5x + 2 = x3 x2 - 5x + 2 - x3 = 0 -x3 + x2 - 5x + 2 = 0 If we change the sign of these equation then, x3 - x2 + 5x - 2 = 0 Ans:- 3 No...
-
The - CPH4 Here , in this blog you get the complete detail about the CPH4 . The CPH4 stands for 6 - carboxytetrahydropterin synthase , this...
-
i) The linear relationship in between electrical control signal and the rotor speed over a wide range. ii) The inertia of rotor should be a...
-
Hi friends my name is Rajakumar, I am the student of Government Polytechnic Mumbai. As like ever...
-
Hello dear all readers, Welcome to this new blog post concept, here you come to know that the merits and the demerits of the 'Huygens...
-
Here we come to know about the Huygen's construction of spherical wavefront. So let's come to know, i) The spherical wavefront is fo...
-
Why we swing our arms when we walking ? Hello dear all my readers , Have you ever think ...