Friday, 5 March 2021
State and explain the main characteristics of the wavefront in easy and simply way.
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
What is the expecting wavefront shape when the portion of the wavefront of light from a distant star intercepted by the earth ?
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Thursday, 4 March 2021
What is the expecting shape of the wavefront when light emerging out of a convex lens ?
Hello dear all readers,
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
What is the expecting shape of the wavefront when light diverging from a point source ?
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Wednesday, 3 March 2021
What are the main characteristics of the wave normal !!!
Hello dear all readers,
Welcome to this concept, so here in this concept you come to know about the main characteristics of the wave normal in easy and simple way.
So let's come to our topic,
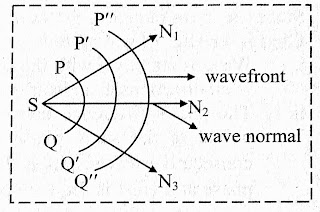
i) The wave normal gives the direction of propagation of wave.
Let's take an one example, the medium through which wave is propagated, for an example 'air' so the wave is move in the direction of air simply.
Actually medium or we can say channel gives the direction for propagation of wave.
So it means that, the wave normal work according to the medium through which is allow to propagate.
ii) The wave normal is perpendicular to the wavefront.
Explanation : As you can see in the given image, the wave normal is perpendicular to the wavefront.
It means that, the wave normal make an angle with wavefront is 90° Degree.
iii) In a homogeneous isotropic medium, the wave normal is same as direction of ray of light.
Explanation : In a homogeneous isotropic medium or channel, the wave normal is same as direction of light.
It means that , First of all we have to know that, what is homogeneous ?
Homogeneous : Homogeneous is a uniform structure.
Isotropic material : The isotropic material whose properties remains same when tested in different different directions.
When we allow to propagate wave normal in the Homogeneous isotropic medium then the direction of the wave normal is in the direction of ray of light.
iv) Wave normal is drawn from the point of generation of wavefront.
Explanation : Actually the wave normal is start from the point where wavefront is generated.
So we hope you understand this concept very simply and easily.
If you have any doubt related to this concept than feel free to ask us.
We feel good to reply you as soon as possible.
Goodbye !!!
Thank you...!!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Tuesday, 2 March 2021
State the different types of wavefront with suitable examples !!!
Hello dear all readers,
Welcome to this concept, so in this concept you come to know the different types of wavefronts with examples.
So let's explore this concept !!!
The wavefront is three types,
i) Spherical wavefront
ii) Plane wavefront
iii) Cylindrical wavefront
So let's know about this different wavefronts with an examples !!!
i) Spherical wavefront : The wavefront which is originating from a point source of light at some finite distance is called as or known as 'spherical wavefronts'
The example of this spherical wavefronts is : The candle flame, which we use in our day to day life in the moments such as birthday, marriage anniversary, or when electricity cut off.
The candle flame glow in the form of spherical wavefront.
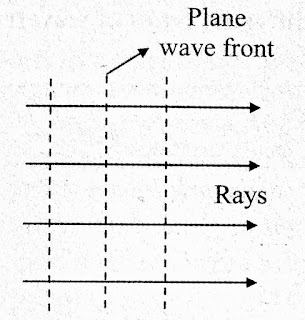
ii) Plane wavefront : The wavefronts which is originating from a point source of light at infinite distance is called as or known as 'plane wavefront'.
The example of this plane wavefront is : The light from the sun arrives at the surface of the earth in the form of plane wavefront.
iii) Cylindrical wavefront : The wavefront which is originating from the linear source or slit of light at some finite distance is called as or known as 'cylindrical wavefront'.
The example of this cylindrical wavefront is : When a tube light is glow, it glow in the form of 'cylindrical wavefront'.
So we hope you understand this concept in simply and nicely.
So if you have any query related to this concept than feel free to ask us.
If in your mind have any idea to know something in simple and easy way than write in the comment box.
Good bye !!!
Thank you...!!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Monday, 1 March 2021
National science day celebrated in the remembrance of physicist C.V Raman !!!
History of The National Science Day
What are the aim of celebrating National Science Day ?
The theme of National Science Day 2021
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Sunday, 28 February 2021
Know complete kepler's laws of planetary motion in simple and easily | By scientechplus
Welcome to this new concept, so here in this concept you will come to know about all kepler's law of planetary motion.
So let's start to know the concept,
So first of all we know that the kepler's first law,
For understanding this kepler's law of planetary motion, first of all we need to know about, what is ellipse ?
So if we talk about ellipse than this ellipse have two foci or we can say two focus point.
This foci is same measure from the centre of the ellipse.
The longer foci diameter is known as or called as 'major axis'.
And the smaller foci diameter is known as or called as 'minor axis'.
So as like that, at one foci the sun is situated and rest of all planet revolve around the sun in elliptical orbit motion.
The second law of kepler's planetary motion : The second kepler's law state that, the line joining the planet and the sun sweeps equal areas in equal interval of time.
The planet which moving from point A to point B and the planet which move from point C to point D, according as you can see in the above given image, so if we calculate both cover area by the planet is same in equal interval of time.
So let's say if we consider, the planet cover 10 metre square in 2 minutes than so in the coming 2 minutes the planet will also cover only 10 metre square area.
I mean to say that, the planet cover equal area in equal interval of time not equal distance.
So this is only possible because of according to the kepler's suggested statement on, "A planet moves faster when it is closer to the sun and the planet moves slowly when it is farther from the sun".
So you have one question arises in your mind that, how it is possible when planet come closer to the sun it moves faster and when it farther from the sun it become slow ?
So the answer is : It is only because of gravitational pull.
When as planet arrives closer to the sun the gravitation pull become more and when the planet farther from the sun the gravitational pull become less.
The third law of kepler's planetary motion : The kepler's third law state that, the square of it's period of revolution around the sun is directly proportional to the cube of the mean distance of a planet from the sun.
The planet as much as time take to revolve around the sun, so square of that time and this is equal to the cube of it's semi major axis.
So we hope you understand this concept very clearly and nicely.
If you have any query related to this concept than please fell free to ask us.
So we will meet you with next upcoming interesting concept.
Goodbye !!!
Thank you...!!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Define about wavefront, wave normal and wave surface in simply and easily | By scientechplus
Hello dear all readers,
Welcome to this concept, so here in this concept you come to know the definition about wave front, wave normal and wave surface.
So let's define first of all 'wavefront'
i) Wavefront:- The locus of all the points of the medium to which waves reach simultaneously so that all the points are in the same phase or we can say all the points in same state of vibration is called as or known as 'wavefront'.
And the second is 'Wave normal'
ii) Wave normal:- A perpendicular line drawn to the surface of a wavefront at any point of the wavefront in the direction of propagation towards light waves is called as or known as 'wave normal'.
And the last third is 'Wave surface'
iii) Wave surface:- The surface of a sphere with light source as centre and distance travelled by light waves as radius where each waves reach simultaneously is called as or known as 'wave surface'.
So we hope you understand this concept very simply and nicely.
So we will meet you in next upcoming interesting concept.
Goodbye !!!
Thank you...!!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Popular Posts
-
Ans : 1) This method cannot give the error, if inputs are other than the 3 standard test inputs. 2) Most of the times, this method gives ma...
-
The Applied Electronics MCQ || Test Revision paper !!! 1) The types of coupling used in the BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) amplifier. a)...
-
Controlled Rectifier: i) When SCR are used to convert AC to DC they have controlled output voltage, so it is called a controlled rectifier...
-
x2 – 5x + 2 = x3 x2 - 5x + 2 - x3 = 0 -x3 + x2 - 5x + 2 = 0 If we change the sign of these equation then, x3 - x2 + 5x - 2 = 0 Ans:- 3 No...
-
The - CPH4 Here , in this blog you get the complete detail about the CPH4 . The CPH4 stands for 6 - carboxytetrahydropterin synthase , this...
-
Here we come to know about the Huygen's construction of spherical wavefront. So let's come to know, i) The spherical wavefront is fo...
-
i) The linear relationship in between electrical control signal and the rotor speed over a wide range. ii) The inertia of rotor should be a...
-
Hi friends my name is Rajakumar, I am the student of Government Polytechnic Mumbai. As like ever...
-
Hello dear all readers, Welcome to this new blog post concept, here you come to know that the merits and the demerits of the 'Huygens...
-
Why we swing our arms when we walking ? Hello dear all my readers , Have you ever think ...