Monday, 22 March 2021
Today's 2021 year play Holi festival with corona virus with some taking precaution !!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Tuesday, 9 March 2021
Explain the refraction of light on the basis of wave theory and also prove the laws of refraction of light.
i) The incident rays, refracted rays and normal lie in the equivalent plane.
ii) The incident ray and refracted ray lie on opposite sides of normal.
iii) The ratio of velocity of light in rarer medium to velocity of light in denser medium is a constant called refractive index of denser medium with respect to rarer medium.
Explanation laws of refraction :
i) Let consider XY be the plane refracting surface separating two media air and glass of refractive indices μ1 and μ2 serially.
ii) A plane wavefront AB is developing at an angle towards XY from the air medium. It is bounded by the rays AA1 and BB1 which are incident rays.
iii) When point 'A' reaches 'A1' then point 'B' will be at 'P'. It even now has to cover distance PB1 to reach XY.
iv) According to Huygens' principle the secondary waves will originate from A1 and will spread over a hemisphere in the glass.
v) All the rays between AA1 and BB1 will reach XY and spread over the hemispheres of increasing radii in the glass. The surface of tangential of all such hemispheres is RB1. This allow to rise refracted wavefront B1R in the glass.
vi) A1R and B1R1, are refracted rays.
vii) Let consider c1 and c2 be the velocities of light in air and glass .
viii) At any instant of time 't' distance covered by the incident wavefront from point P to B1 = PB1 = c1t.
The distance covered by the secondary wave from point A1 to R = A1R = c2t.
Proof of laws of refraction:
angle AA1M + angle MA1P = 90° .................................(1)
and angle MA1P+ angle PA1B1 = 90° ...........................(2)
From equations (1) and (2),
angle AA1M = angle PA1B1 = i
ii) Similarly, angle NA1R = angle N1B1R1 = r
We have, angle N1B1R1 + angle N1B1R = 90°.............(3)
and angle N1B1R + angle A1B1R = 90° ......................(4)
From equations (3) and (4)
angle N1B1R1 = angle A1B1R = r
iii) In triangle A 1PB1, sin i = PB1/A1B1 = c1t/A1B1................(5)
iv) In triangle A1RB1, sin r = A1R/A1B1 = c2t /A1B1..............(6)
v) Dividing equation (5) by (6),

Therefore sin i/ sin r = c1/ c2....................(7)
Also c1/ c2 = μ2/ μ1 = 1μ2 ......................(8)
Where as 1μ2 = R.I. of water with respect to air,
sin i/ sin r = μ2/ μ1
vi) From the explanation, it is clear that incident rays AA, BB, refracted rays A,R, B,R and normal MN and MIN lie on the same plane XY. Also incident ray AA, and refracted ray AR lie on opposite sides of normal MN. Therefore, laws of refraction can be explained.
THE END
Thank you
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Sunday, 7 March 2021
With the help of a neat diagram | explain the reflection of light from the plane reflecting surface on the basis of wave theory of light.
So here first of all we know that,
What is the laws of reflection :
i) In the laws of reflection, the incident rays, reflected rays, and normal to the reflecting surface at the point of incidence, all lie in the same level.
ii) In the laws of reflection, the incident rays and the reflected rays lie on the opposite sides of the normal.
iii) The angle of incidence is equal or we can say equivalent to the angle of reflection.
For clear understanding the law of reflection in simple and easy way. So for that lets see the simple explanation about all these points.
Explanation :
i) The plane wavefront AB is developing at an angle towards plane reflecting surface XY.AA1 and BB1 are incident rays.
ii) When point 'A' come to XY at A1, than ray at 'B' reaches at point P and it has to cover distance PB1 to reach the reflecting surface XY.
iii) Let's consider 't' be the time to required to cover distance PB1.
In this time meantime, the secondary waves are emitted from the point A1 and it will spread over the hemisphere of the radius A1R in the same medium.
The distance covered by the secondary waves to reach from A1 to R in time 't' is same as the distance covered by the primary waves to reach from point P to B1.
So therefore A1R = PB1 = ct.
iv) All other rays in between AA1 and BB1 will reach XY after A1 and before B1. Therefore they will also emits secondary waves of the decreasing radii.
v) The surface touch all such hemispheres is RB1 which is reflected wavefront, bounded by the reflected rays A1R and B1Q.
vi) Let's draw A1M perpendicular to XY and B1N perpendicular to XY.
Thus, the angle of incidence is angle AA1M = angle BB1N = i and the angle of reflection is angle MA1R = angle NB1Q = r.
angle RA1B1 = 90 - r
angle PB1A1 = 90 - i
vii) In the triangle A1RB1 and triangle A1PB1
Here angle A1RB1 congruent to angle A1PB1
A1R = PB1,............ (Reflected waves travel in equal in same medium in equal time).
A1B1 = A1B1.........(Common side)
Therefore triangle A1RB1 congruent to triangle A1PB1
Therefore angle RA1B1 = angle PB1A1
Therefore 90 - r = 90 - i
Therefore i = r
viii) From the above given figure, it clear that the incident ray, reflected ray and normal lie in the same level or plane.
ix) This laws of reflection of light from the plane reflecting surface on the basis of Huygen's wave theory.
THE END
Thank you
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Saturday, 6 March 2021
The Huygen's construction of spherical wavefront in simple and easy way !!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Explain the Huygen's construction of plane wavefront in easy and simple way !!!
Explain the Huygen's construction of plane wavefront in easy and simple way !!!
So let's come to know,
i) The plane wavefront is formed when the point of observation is very far away or we can say at infinity from the primary source of light.
ii) So here let's PQR represent a plane wavefront at any instant.
So according to the Huygen's principle, all the points on this wavefront will act as a secondary source of light and sending out secondary wavelets in the forward direction only.
iii) For make it to undestand easily, first of all we need to draw hemisphere with Point P,Q,R.... as centres and 'ct' as a radius.
The surface tangential to all such hemisphere is P1Q1R1....at instant 't'.
The new wavefront at time 't'.
iv) The plane wavefront is propagated or travel as a plane waves in the homogeneous isotropic medium. Therefore they are parallel to each other.
v) PP1N1, QQ1N2, RR1N3 these are the wave normal at point P,Q,R respectively.
These wave normal shows the direction of propagation of the plane wavefront.
vi) The new wavefront P1Q1R1 is parallel to the primary wavefront PQR.
THE END
Thank you....!!!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Difference in between primary source of light and secondary source of light in easy way !!!
Primary source of light
i) The primary source of light is a real source of light.
ii) Primary source of light sends out primary waves in the all possible directions.
iii) The primary source of light is effective at every point on it's surface.
iv) The primary source of light is situated in the air.
The secondary source of light
i) The secondary source of light is a fictitious source of light.
ii) The secondary source of light sends out secondary waves only in the forward direction.
iii) The secondary waves is effective only at the points where it touches the envelope.
iv) The secondary source of light is situated on the wavefront.
THE END
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Friday, 5 March 2021
State what are the Huygen's principle statement !!!
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
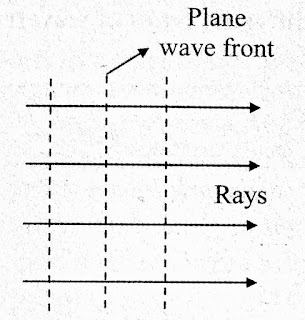
State and explain the main characteristics of the wavefront in easy and simply way.
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
What is the expecting wavefront shape when the portion of the wavefront of light from a distant star intercepted by the earth ?
 Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Hello friends my name is Rajakumar Dayashankar Gupta . Here I am started to write blog on name scientechplus . I am started to writing this blog post on science , technology and engineering since 2020 . I completing my ssc , than after I go for stream in science field , than after completing my 12th science than later I realize my self , I am interested in electronics fields , so I start learning in diploma electronics engineering . My journey is quite interesting to choosing right decision of my aim . And I want to explain the concept in simple and precise way . I every time want to learn something new , it means that something new from open minded from our environment . To learn something new from our expectation . It quite special and very interested to hear that , when we imagine or think we go to learn something very uniqueness our eyes fill with glow , that moment is such a very great pleasurable moment we feel isn't it ? . And I want to share the information , facts , knowledge related to all science , technology and engineering in detail , simple and precise way .
Popular Posts
-
Ans : 1) This method cannot give the error, if inputs are other than the 3 standard test inputs. 2) Most of the times, this method gives ma...
-
The Applied Electronics MCQ || Test Revision paper !!! 1) The types of coupling used in the BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) amplifier. a)...
-
Controlled Rectifier: i) When SCR are used to convert AC to DC they have controlled output voltage, so it is called a controlled rectifier...
-
x2 – 5x + 2 = x3 x2 - 5x + 2 - x3 = 0 -x3 + x2 - 5x + 2 = 0 If we change the sign of these equation then, x3 - x2 + 5x - 2 = 0 Ans:- 3 No...
-
The - CPH4 Here , in this blog you get the complete detail about the CPH4 . The CPH4 stands for 6 - carboxytetrahydropterin synthase , this...
-
Here we come to know about the Huygen's construction of spherical wavefront. So let's come to know, i) The spherical wavefront is fo...
-
i) The linear relationship in between electrical control signal and the rotor speed over a wide range. ii) The inertia of rotor should be a...
-
Hi friends my name is Rajakumar, I am the student of Government Polytechnic Mumbai. As like ever...
-
Hello dear all readers, Welcome to this new blog post concept, here you come to know that the merits and the demerits of the 'Huygens...
-
Why we swing our arms when we walking ? Hello dear all my readers , Have you ever think ...